Content Quick Overview

What Will You See If WiFi is Connected but No Internet Connection?
Many WiFi users have complained that their WiFi is connected but no internet connection. In most cases, this happens when they try to use WiFi in a public environment such as airports and hotels.
When you have an internet error in a public network, I would first warn you that connecting to a wireless network in a public place is dangerous. Then it is probably because your network firewall is blocking the transmission of the public network signals. However, it also happens when they connect to WiFi at home or in the office.
When you encounter this situation: “WiFi is connected but no internet connection,” you can determine your judgment in two simple ways.
- Router
- Your connected devices
By router: If all the devices connected to the network cannot access the internet, then it is likely that your router/modem has a problem. You can determine by your router’s signal indicator if there is a network your router signal light will blink faster when you have a wireless network problem. Your router light will flash slowly or even not.
By your connected devices: When you connect to the network with your laptop after you connect successfully, your network signal is normal, but under the name of your network connection, it shows No Internet access. And you open the browser; you can’t search anything, the browser will show No Internet.

Why is Your WiFi is Connected but No Internet Connection?
Actually, network connections problems are not as complicated as you think. Several factors make Wi-Fi connection to the internet was unsuccessful, such as:
- IP address conflict.
- Wi-Fi router/modem has no Wi-Fi.
- Anti-virus or Other Security App stop your internet connection.
- Overdue broadband tariff payment.
- The Network adapter is overdue.
- Wi-Fi is turned off by default on your wireless router/modem.
The absence of network connectivity can be attributed to a myriad of factors, as delineated in this abridged compilation of prevalent network dilemmas encountered in various scenarios. Predominantly, conflicts in IP addresses stand as the principal catalyst for the phenomenon of WiFi connectivity devoid of network access. Subsequent sections will elucidate methodologies aimed at addressing and rectifying these typical causations.
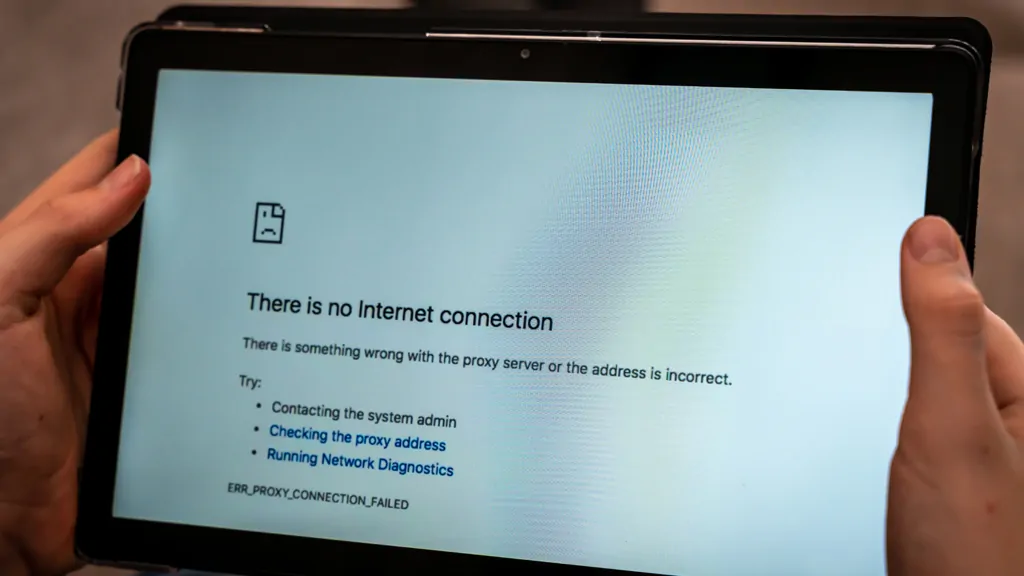
IP Address Conflicts Will Result in “No Internet”
For computers to communicate with each other over the network, they must have a legitimate IP address. Suppose your WiFi is connected but no internet connection. In that case, the first and most obvious reason is that another PC or device has used your IP address. If this happens, you will have to find out the other computer’s IP address. Then you can change it back to ensure that there are no conflicts with the network.
IP address = network address + host address
Simply put, an IP address is the same as your home address. Comparing the internet to the real world, when someone sends you a letter, he needs to know your address to send the letter to you. Likewise, when someone sends you a message, the Internet host needs to know your IP address to send the message to you accurately.
How to Resolve IP Address Conflicts?
Please note that only devices connected to your network may cause IP address conflicts. For example, suppose only one device is connected to your network. In that case, no internet is unlikely to be caused by an IP address conflict unless someone is secretly rubbing the internet.
Change Your IP Addresses
As delineated previously, the uniqueness of IP addresses is paramount within a network ecosystem, with each network participant and their respective devices being assigned a distinct IP address. Consequently, the occurrence of duplicate IP addresses, where two devices inadvertently share the same IP, precipitates complications for the network infrastructure. Addressing this issue through the modification of the conflicting IP addresses serves as a remedial measure to restore network functionality.
The following operation uses Windows 7 as an example:
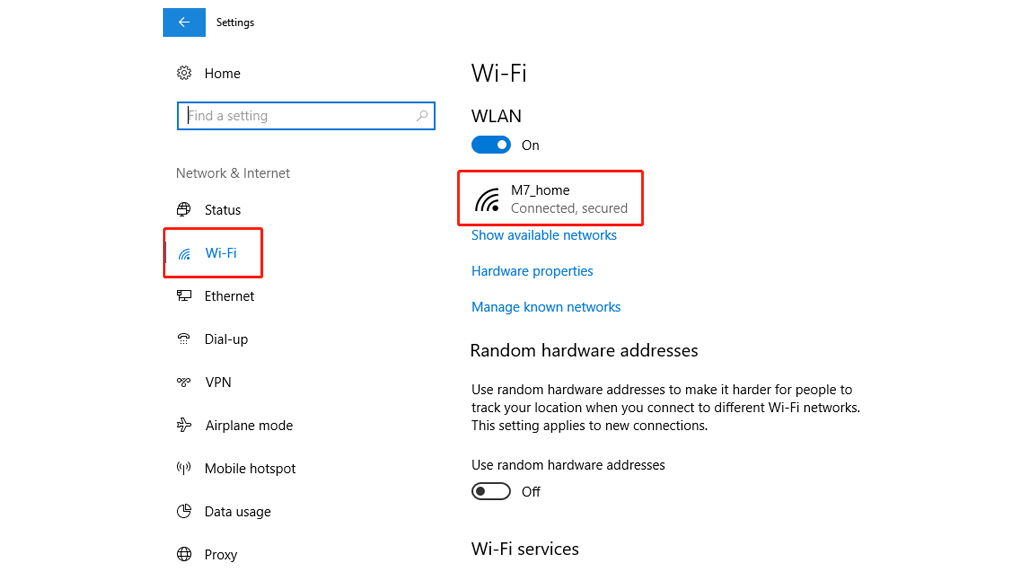
- Make sure your devices are connected to the internet
- Open the Computer Settings > click the Network&Internet > Wi-Fi > chose your connected network > IP settings
- If your IP assignment is Manual, change it to DHCP
- Click save
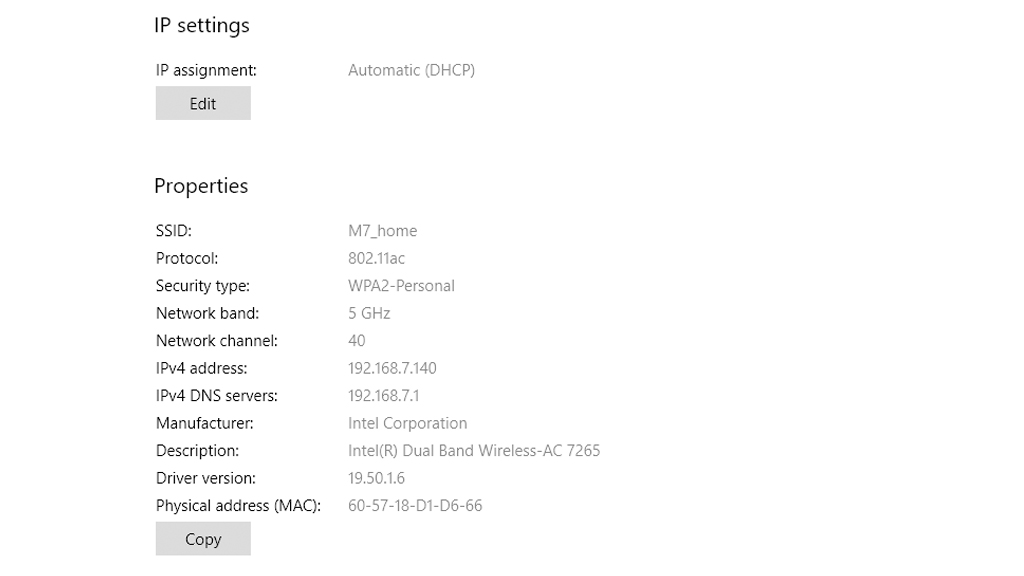
There are two ways to set the IP address of your computer: manual and DHCP. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) means automatic setting, the manually assigned IP address will not change unless you change it. DHCP will automatically get available and not duplicate IP addresses. The Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP/IPv4) is shown with your IP address.
No IP Conflicts? Check This Points to Fix Your Network
If you find that your modified IP settings and your network still don’t work, then it’s probably not a problem with IP address conflicts. Since there are many reasons for no network, The following method is also to fix your network. If your network is slow only, you can check the article “How to improve your network” to boost your network speed.
Method 1: Restart Your Wireless Router
An excellent way to fix your router is to reboot it. While this may sound silly, a reboot can refresh the cache and fix many interconnected network and software problems. Rebooting your router will also allow your WiFi to reacquire an IP address, provided that you have set up an IP address automatically.
Note: If your router and modem are separate, you will need to reboot them both.
- Turn them both off
- Wait 30 seconds
- Turn on the modem, and then turn on the router after 1 minute.
- Wait a few minutes and check.
- This simple solution will solve many minor problems in your router.
Method 2: Check Your Modem Lights
Numerous WiFi users overlook the diagnostic potential of their modem’s indicator lights. These lights on your WiFi modem/router serve as a visual representation of the current status of your WiFi connection, offering invaluable insights into its operational state. Furthermore, they play a crucial role in troubleshooting WiFi-related issues. To leverage this feature for the identification of WiFi network anomalies, there exist multiple methodologies for interpreting the WiFi router’s light indicators, each providing a pathway to detect and subsequently address connectivity challenges.
Under typical circumstances, the illumination of the WAN (Wide Area Network) light on your modem signifies the establishment of a wired connection, indicating successful connectivity to the broader internet. A slow, periodic blinking of the modem’s Wi-Fi light is indicative of a properly functioning Wi-Fi network, signaling active and stable wireless connectivity. Conversely, a persistently rapid blinking—or the absence of light—from the Wi-Fi indicator may denote issues pertaining to the Wi-Fi network or
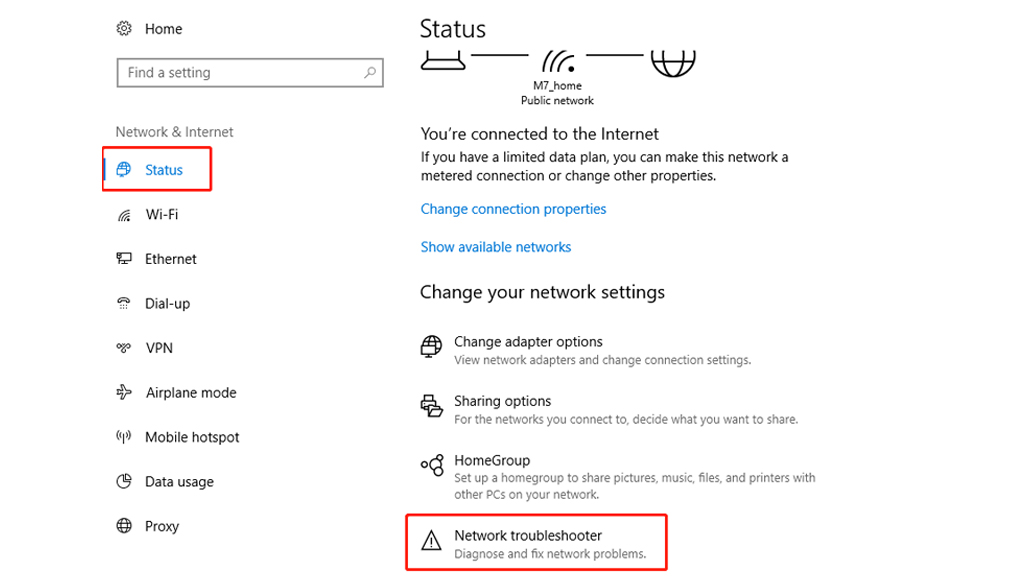
Method 3: Using Network Troubleshooter
Troubleshooting your network can also rely on the network troubleshooter inside your device, you can run the network troubleshooter that came with your computer as follows.
Here is the operation interface of Windows 10 as a reference. If you have other versions of Windows, please check the operation method of different versions here.
- Select the Windows button, and then find the settings section.
- Select Settings > Status > Network Troubleshoot > Click the Network Troubleshooter button.
Method 4: Shutdown Your Antivirus or Security App
Anti-virus or security software is likely blocking your WiFi. Excessive security can significantly affect your WiFi network because most WiFi connections rely on port forwarding, which requires opening ports to transfer data. However, you can go to the anti-virus settings, find the WiFi section, and then turn on the network access.

Don’t download anti-virus software at random, restore your Wi-Fi configuration. Don’t download random anti-virus software, some of which will not only clog your network but also slow down your computer and seriously affect your Internet experience.
Note that this is not to say that you don’t need any anti-virus software, or that network security firewalls are unimportant. However, if your computer system is genuine, the computer’s firewall is sufficient to meet most people’s network security needs.
Method 5: Change Your Router’s Wireless Mode
It’s not uncommon for this to be the case that your connected device is too old. For example, suppose you get Internet access on your PC by connecting to the router via an Ethernet cable. In that case, there may be a communication barrier between these two devices. Changing the wireless mode (2.4GHz and 5GHz) is one way to solve this problem.
There are several wireless modes available on the router. For example, you may have seen something like 802.11 b or 802.11 b/g or 802.11 b/g/n/ac/ax, etc. The b, g, n, ac, and ax inside these different parameters represent different wireless standards. Usually, the wireless mode is set to 802.11 b/g/n/ac, which works properly for most users. Occasionally, devices like some older smartphones are not compatible with this mode of 802.11 ax, causing network problems.
In the same vein, the Speedefy KX450 WiFi 6 router is used as a demonstration of operation:
- Log in to the Speedefy router’s web management page
- Chose WiFi Settings > Channel & Bandwidth
- In the 5 GHz Network section: Click the Network Mode
- Change the mode to 802.11 a/n/ac
- Reconnect the WiFi network
Method 6: Reset Your Wireless Router
This option will solve almost all router-related issues. You can reset the router to factory settings, forcing a reset of all new changes that could cause problems. Similarly, this means that you must password protect your router again and change the basic settings to suit your needs.
The reset method varies slightly from router to router, but the sequence of operations is similar. If you have a Speedefy router, you can refer to this article, “How to reset your router.“
The primary sequence of operations for all types of routers is as follows:
- Put the reset button>log in to your router’s web interface>set up the Wi-Fi name and password>Set up your wireless router’s setting as you want.

Method 7: Your ISP is Expired or Down
Call your internet provider, let them check your Wi-Fi, ask them to help you solve the problem. Your internet service provider may have been expired or something else wrong with your service.
People often pay for internet for six months or a full year. It’s much better to pay for long-term internet service at once, and you don’t always need to get a reminder of your bill. So you may be in a situation where your internet service expires. Still, you don’t know about it, and you don’t get any reminders. Maybe you have emails from your ISP in your junk mailbox, but you don’t see them.
Even if your internet service is expired, you can still connect to WiFi, but you won’t have any internet. Your internet is not valid. Many people have checked various network causes and finally found out that the problem is in their memory.

Method 8: Check Your Wireless Network Adapter Driver
In most cases, WiFi problems are caused by a faulty WiFi adapter driver. In Device Manager > Network Adapters, a WiFi Adapter should be listed under this section if it is working correctly. If WiFi is not listed here, update your wireless network device drivers or uninstall, then reinstall the wireless network adapter.
Method 9: Reset Your Network Settings
And if WiFi still fails to work, reset your WiFi network settings. On Windows 10, go to Settings>Network & Internet>WiFi>Manage WiFi Settings>Advanced Options>Restore WiFi Defaults.
Network reset will remove all Wi-Fi settings like Wi-Fi networks and Wi-Fi preferences that you have saved. This method is straightforward to implement, but the downside is you’ll need to reconfigure your Wi-Fi network after resetting.
Wrap-up: Most Causes Have Been Resolved
There is no single answer to the problem of Wi-Fi being connected but no Internet access. From the most specific IP address, DNS server, ethernet cable connection errors, changes can cause you not to connect to the internet properly, and the tips above should solve most software-related problems. However, you will have to contact a technician if it is a hardware problem – such as a broken wireless network adapter or router.
